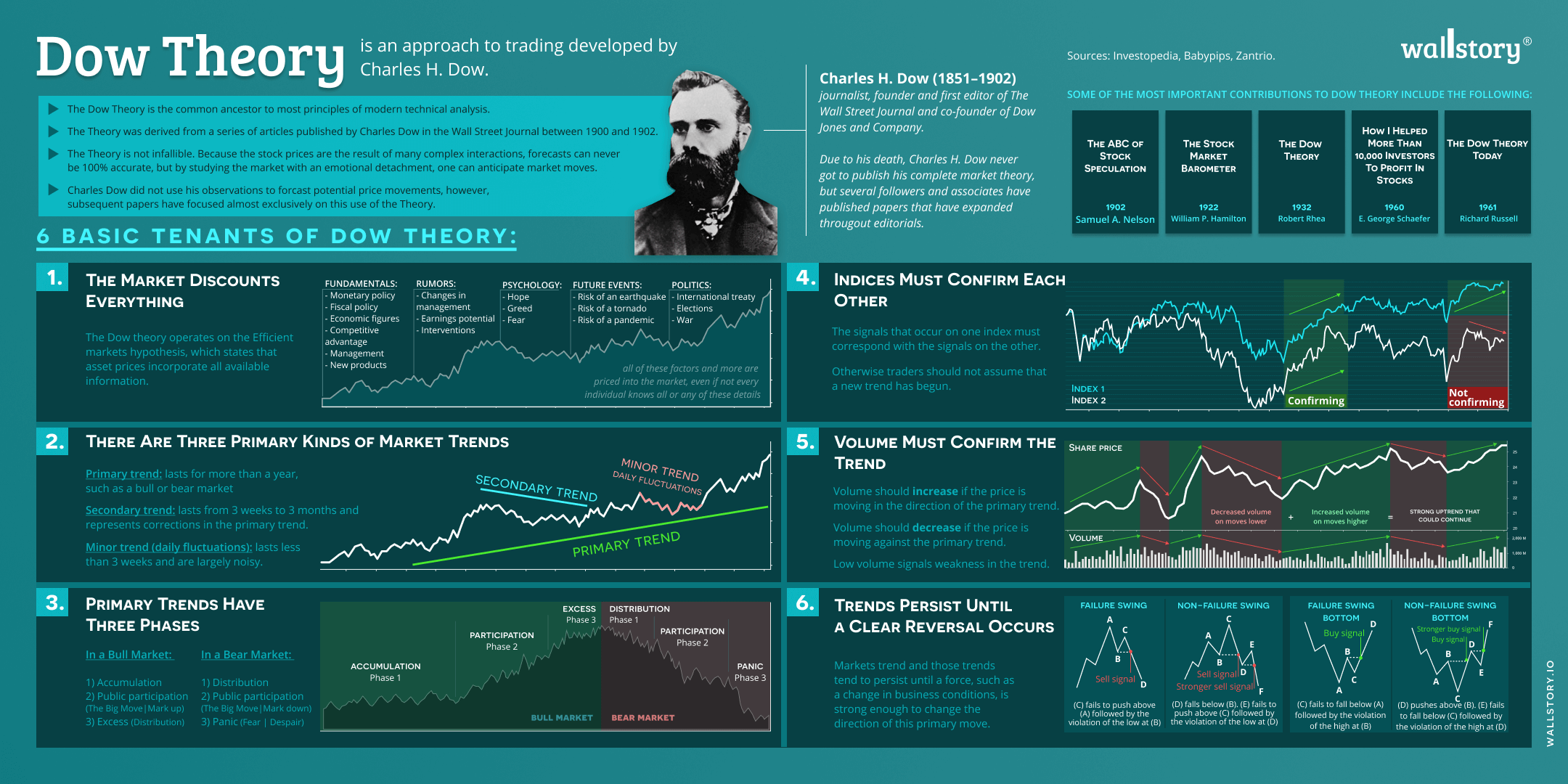
The Dow theory is a market theory developed by Charles Dow, co-founder of The Wall Street Journal, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It is considered to be one of the earliest and most influential market theories and is still widely followed by traders and investors today. The theory outlines several key principles that are still widely used by market participants to analyze and understand market trends and make investment decisions. The Dow theory is based on six key principles: 1. The market has three trends: primary trends, secondary or intermediate trends, and minor trends. 2. The market averages must confirm each other. In other words, if one average is rising, the other should also be rising, and vice versa. 3. Trends are more likely to continue than to reverse. 4. Volume must confirm price movements. A rising market should be accompanied by increasing volume, and vice versa. 5. The market discounts everything. All relevant information, both bullish and bearish, is already reflected in the market's current price. 6. Trends exist until definitive signals indicate a change.







